Scalable Scientific Machine Learning Lab
@ Imperial College London
We accelerate science by building robust, scalable scientific machine learning algorithms.

Latest News 🚀
-
3 papers accepted at Differentiable Systems and Scientific Machine Learning workshop @EurIPS 2025

We are excited to announce we have 3 workshop papers accepted at the Differentiable Systems and Scientific Machine Learning workshop at EurIPS on December 6,… Read more →
-
Dr. Ben Moseley gives workshop on scalable physics-informed neural networks at CWI Amsterdam

Dr. Ben Moseley taught students how to design scalable physics-informed neural networks at Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica in Amsterdam during their Autumn School on Scientific… Read more →
-
We’re hiring PhD students!

Several PhD opportunities are available in our Scalable Scientific Machine Learning Lab at Imperial College London. These projects are eligible for Imperial PhD scholarships (open… Read more →
-
Ardan Suphi visits University of Bern

One of our PhD students, Ardan Suphi, will be visiting the University of Bern to collaborate on improving multispectral imaging of Mars using SciML. He… Read more →
-
Dr. Ben Moseley joins editorial board of new ACM journal on AI for science

We’re excited to share that Dr. Ben Moseley has joined the editorial board of the new ACM Transactions on AI for Science (TAIS) as an… Read more →
-
New SciML lab at Imperial College London!

We are very excited to announce the formation of our new research group, the Scalable Scientific Machine Learning Lab. The group is led by Dr.… Read more →
Project Highlights 🌍
-
Multi-scale simulation with physics-informed neural networks

Overview Physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) have emerged as a promising tool for solving differential equations. They have been applied to many scientific problems and a… Read more →
-
SciML-enhanced planetary exploration: advancing lunar and martian imaging

Overview Scientists and engineers leading missions like NASA’s Artemis program and future Mars expeditions, along with planetary researchers studying our solar system’s evolution, rely heavily… Read more →
-
Machine learning with geodesic flows

Overview Many physical, biological and engineering systems evolve over time according to geometric laws, for example planets follow elliptical orbits shaped by gravity, and fluids… Read more →
-
Efficient and differentiable population balance modelling with JAX

Overview Population balance equations (PBEs) are used to model the evolution of populations of particles over time, such as in crystallisation processes, chemical reactors, and… Read more →
-
Extending quantum theories with AI

Overview Quantum theory is incredibly powerful for predicting the probabilities of what we’ll see in experiments, but it cannot tell us the certain outcome of… Read more →
-
Weather and climate modelling with neural differential equations

Overview This is a new direction for the lab – more to come! Team & collaborators Read more →
Latest Publications 📊

A differentiable hybrid modeling approach for learning soil water retention mechanisms from partial knowledge and data.
Reframed how soil water retention is modelled by augmenting traditional modelling with machine learning components that learnt previously uncertain physics directly from data. Using this method, we accurately reproduced soil water retention behaviour and uncovered new pore-scale insights.
Norouzi, S., Moldrup, P., Moseley, B. et al (2026).
Journal of Hydrology.
Paper
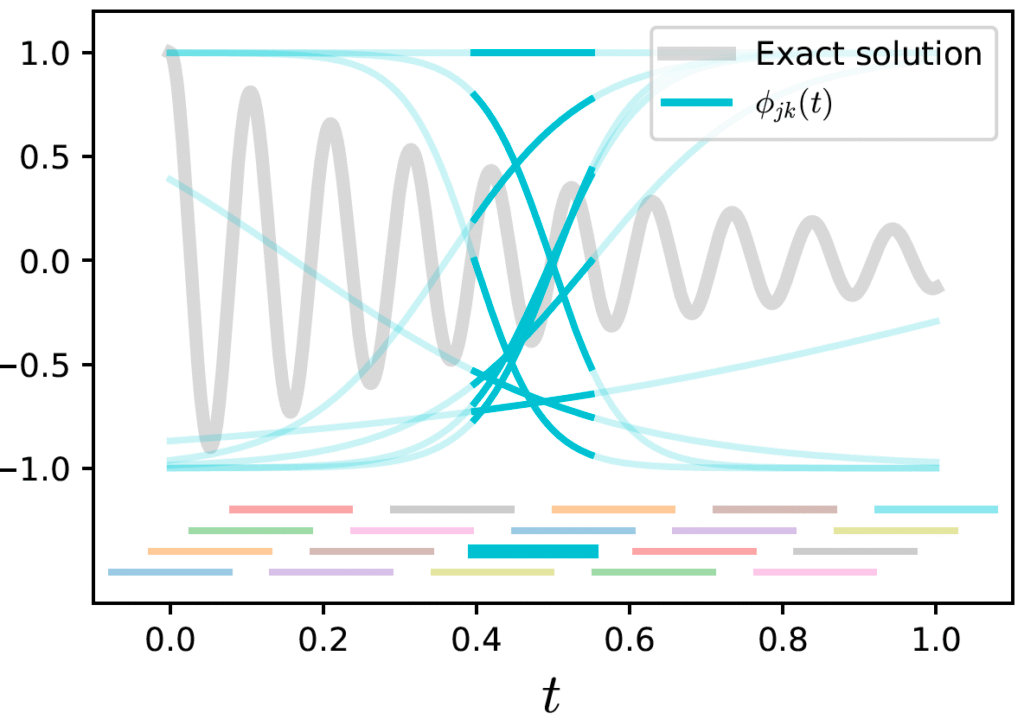
Local Feature Filtering for Scalable and Well-Conditioned Domain-Decomposed Random Feature Methods.
Significantly accelerated the training of physics-informed neural networks by using random features and domain decomposition to turn their optimisation problem into a structured least squares problem and proposing a novel preconditioner to accelerate convergence.
Willem van Beek, J., Dolean, V., Moseley, B. (2025).
Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering.
Paper Code Workshop
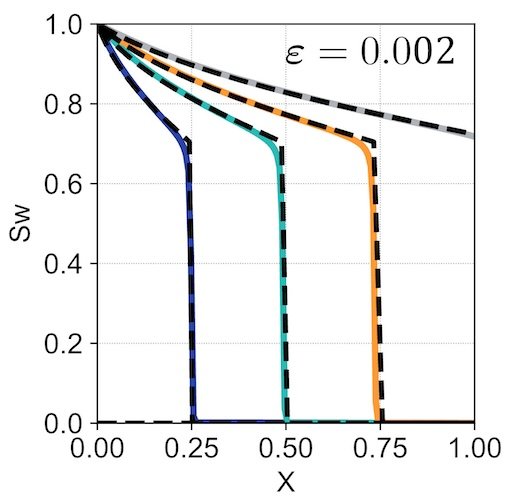
Challenges and advancements in modeling shock fronts with physics-informed neural networks: A review and benchmarking study.
Explores how to improve physics-informed neural networks for solving equations that involve sudden physical changes – like shock waves – highlighting their current limitations and the need for better techniques to handle complex problems accurately.
Abbasi, J., Jagtap, A., Moseley, B., Hiorth, A., Andersen, P. (2025).
Neurocomputing.
Paper Preprint
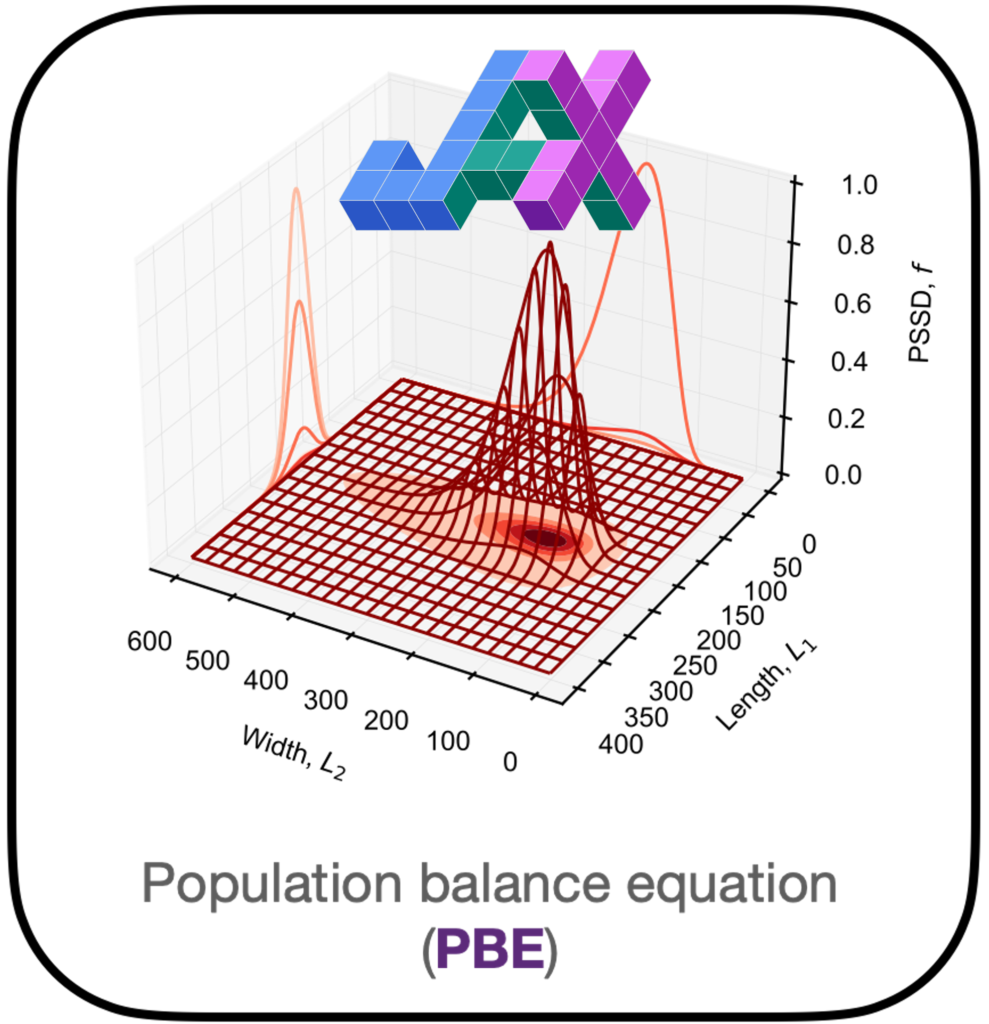
Modern, Efficient, and Differentiable Transport Equation Models Using JAX: Applications to Population Balance Equations.
Alsubeihi, M., Jessop, A., Moseley, B., Fonte, C.P., Rajagopalan, A.K. (2025).
Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research.
Paper
The Team 🎯
Collaborators ✨

Interested in collaborating with us?
